Since iOS 2.0 we have been using UIWebView. UIWebView. fulfill our browsing requirements, loading HTML pages, showing pdf or doc files etc. From iOS 8.0 Apple has deprecated UIWebVew and introduced WKWebView. WKWebView comes under WebKit framework. Below are the advantages of WKWebView
– WKWebView runs faster than UIWebView
– WKWebView runs in a separate process instead of app main process.
– More responsive touch than UIWebView
– WKWebView is more secure than UIWebView, and it supports server-side authentication
– Javascript runs faster in WKWebView
and many more
Not let’s start WKWebView integration. Create a new project and choose Single View App. Now go to Main.storyboard and drag and drop a WKWebView. Create a outlet of WKWebView and name it webView. Import WebKit framework in your class. Now add below code in your UIViewController
@IBOutlet weak var webView: WKWebView!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
let webaddress = "https://www.google.com/" // 1
if let url = URL(string: webaddress) { // 2
let urlRequest = URLRequest(url: url) // 3
self.webView.load(urlRequest) // 4
}
1. Write a web address url that you want to load.
2. We create an object of URL class using webaddress. URL class is having a function public init?(string: String) with returns an optional object, so here we first unwrap the object using if statement.
3. Create an object of URLRequest using URL object.
4. WKWebView have a function to load request and it takesURLRequest an object as a parameter. Now hit run and you will get below screen.
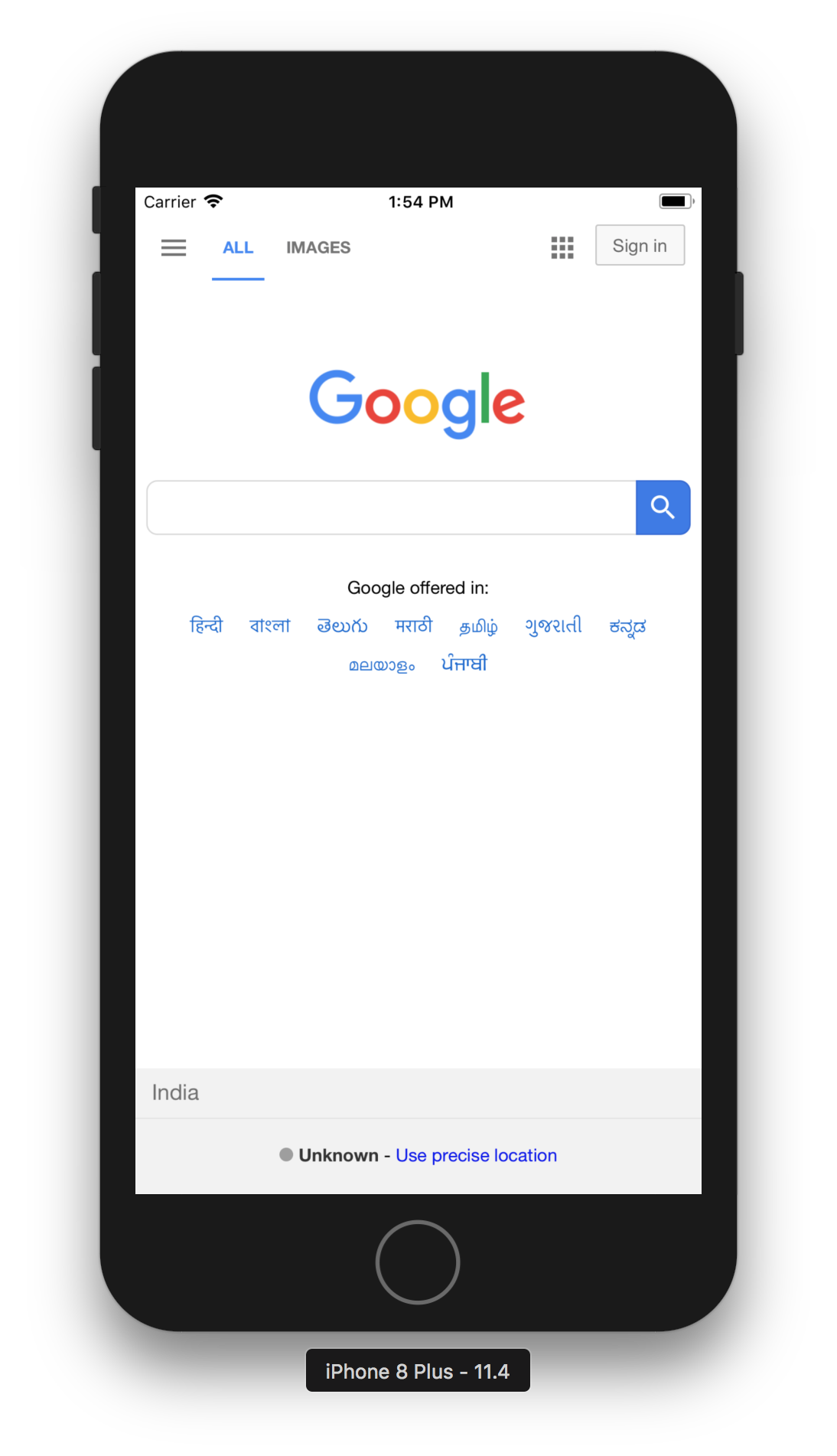
WKNavigationDelegate protocol
WKNavigationDelegate protocol provide functions to track progress and navigation of WKWebView. Now add below line of code in your viewDidLoad function.
self.webView.navigationDelegate = self
Now we need to integrate WKNavigationDelegate in our class. Create an extension of your UIViewController and conform WKNavigationDelegate protocol. Add below code in your class.
extension ViewController: WKNavigationDelegate {
// 1. Decides whether to allow or cancel a navigation.
public func webView(_ webView: WKWebView,
decidePolicyFor navigationAction: WKNavigationAction,
decisionHandler: @escaping (WKNavigationActionPolicy) -> Swift.Void) {
print("navigationAction load:\(String(describing: navigationAction.request.url))")
decisionHandler(.allow)
}
// 2. Start loading web address
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView,
didStartProvisionalNavigation navigation: WKNavigation!) {
print("start load:\(String(describing: webView.url))")
}
// 3. Fail while loading with an error
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView,
didFail navigation: WKNavigation!,
withError error: Error) {
print("fail with error: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
// 4. WKWebView finish loading
func webView(_ webView: WKWebView, didFinish navigation: WKNavigation!) {
print("finish loading")
}
}
Now let’s start discussing these protocol functions.
1. This function lets you decide whether you want to allow navigation or not. If you disallow then it won’t load the new web address. There is closure decisionHandler which takes WKNavigationActionPolicy as a parameter which has two cases cancel and allow. This allows and cancel will decide that navigation should happen or not. As the name indicates.allow, it will allow the navigation and .cancel will disallow it.
2. When WKWebView start loading the page, then this method will get called
3. If there is an error occurred while loading the page, then this function will be called with error details.
4. If WKWebView finished loading successfully then this function will be called.
There are many functions define under WKNavigationDelegate protocol, you can use them as per your requirements.